8 Mins
8 Mins
Share Article
Subscribe and get fresh content delivered right to your inbox

10 Mins
The Software Development Life Cycle in 2026 extends beyond structured phases into real operational complexity. Core stages, major development models, and security integration are examined through practical trade-offs and delivery realities. Attention is given to evolving requirements, governance, maintenance cost, and scalability pressures that influence modern software systems and long-term architectural sustainability across distributed and high-velocity environments.
Continue Reading

10 Mins
AI in design has evolved from a productivity tool into a creative collaborator. This article explores how designers use machine learning and generative tools to automate tasks, accelerate prototyping, personalize experiences, and enhance every stage of the design process. It also examines the skills required, the challenges teams face, and why human judgment remains central as AI reshapes modern creative workflows.
Continue Reading

13 Mins
The experiment phase is over. By 2026, enterprise AI shifts from passive generation to autonomous, governed, and measurable operations, and the window to prepare is narrowing.
Continue Reading
Subscribe and get fresh content delivered right to your inbox
The advent of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) has transformed machines’ ability to comprehend and produce information. When we talk about Gen AI, the first thing that comes to our mind is ChatGPT. ChatGPT is built on a transformer-based architecture, which has features like self-attention (this feature allows the model to focus on different sections of the inputs effectively).
Transformers allow parallel processing and better context handling. Besides, there are different types of Generative AI models, like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), that one should know to make efficient architecture-based decisions when it comes to Gen AI application development.
There are different types of Gen AI models, and they majorly differ on the basis of how each model proceeds to generate content. Let’s see some common types of Gen AI models:
Ian Goodfellow’s proposal in 2014 introduced Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), which are two neural networks put together and termed the generator and the discriminator. The generator’s role is to produce data that resembles real data, while the discriminator’s role is to tell real from false data.
Here are the major components of GANs:

When the generator attempts to deceive the discriminator by producing realistic-looking fake data. However, the discriminator evaluates it by distinguishing between real and generated data.
So, if the generator makes errors, the discriminator learns by identifying those errors and improves its ability to differentiate real data from generated data. This back-and-forth process continues until the generator produces data that the discriminator can no longer distinguish from real data.
This makes GANs highly specialized unsupervised learning models as they can generate highly realistic videos or images without requiring labelled training data.
GANs can help generate stunning and hyperrealistic images and videos, as well as other types of work. They have versatile applications, as they can even easily create fake human faces and artificial data in their applications, suitable for testing purposes.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)’s main purpose is to understand the underlying data distribution, allowing them to create new samples from that distribution. VAEs are different from regular autoencoders. Instead of turning the input into a fixed latent representation, VAEs encode it as a distribution.
Here are the components playing a critical role in VAEs:
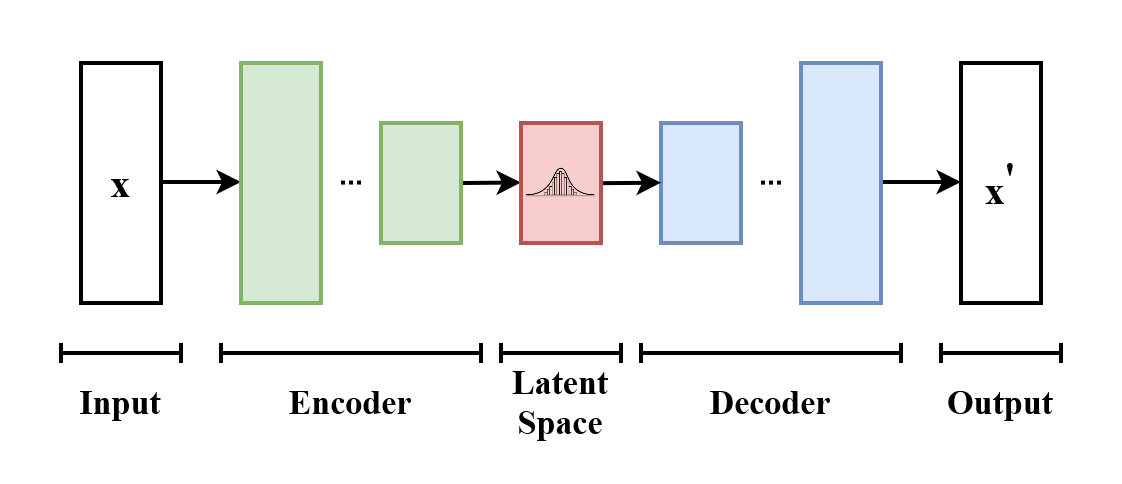 VAEs allow one to generate multiple outputs, making them perfect for use in creative industries. It is generally easier to train VAEs than GANs since there is no competition.
VAEs allow one to generate multiple outputs, making them perfect for use in creative industries. It is generally easier to train VAEs than GANs since there is no competition.
Even though GANs and VAEs are primarily used for image processing, Transformers have taken the Natural Language Processing arena by storm. First presented in 2017, these types of models are good at generating texts, machine translations, and even some forms of images, among many other applications.
Transformers employ self-attention, which enables them to focus on various chunks of the input data irrespective of their length and assign importance to each chunk. This marks a great leap from earlier approaches, such as RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks), which handled input data in a strict order.
Here are the features of transformer architecture:
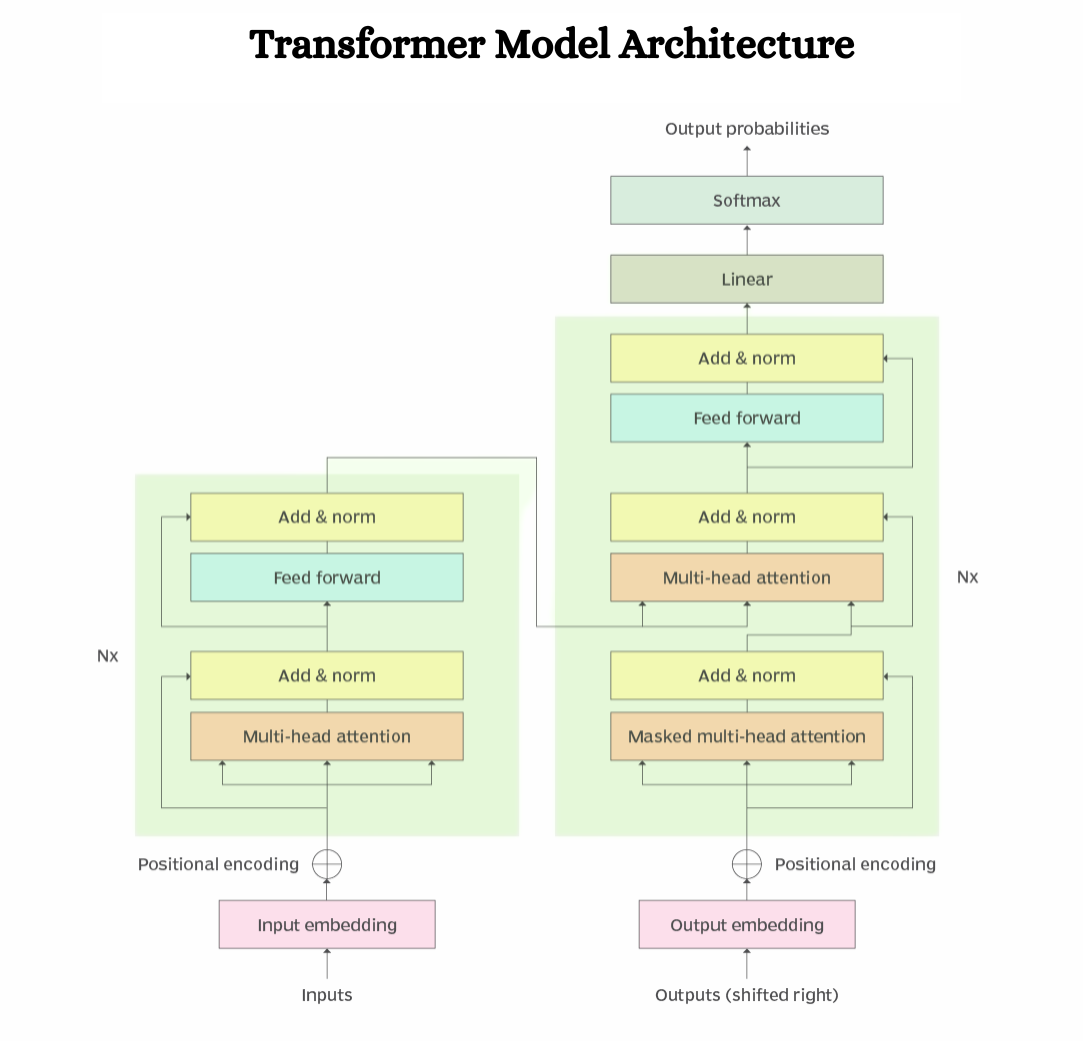
According to the scheme’s tenets, transformers can undoubtedly be effectively deployed to assist processes such as text compression and language transposition because they can handle voluminous data quickly. Transformers can learn long-range relations, which is not the case in RNN models, for instance, which are difficult to understand such long sequences.
Here are the key differences between GANs, VAEs, and transformers:
Features | GANs | VAEs | Transformers |
Architecture | Consists of two networks: a Generator and a Discriminator | Consists of two networks: an Encoder and a Decoder | Composed of Encoders and Decoders with a self-attention mechanism. |
Objective | The Generator tries to fool the Discriminator, while the Discriminator aims to distinguish real from generated sample | Maximize the likelihood of the input data given latent variables while minimizing the discrepancy from a prior distribution | Generating and processing sequences while capturing contextual relationships within data. |
Latent Space | Implicit, typically using random noise as input | Explicit, often modelled as a Gaussian distribution | Implicit, depends on context |
Training Process | Adversarial training, which can be unstable | Likelihood-based training is generally more stable | Comprehensive with multiple stages and os unstable |
Sample Quality | Produces sharp, high-quality samples | Samples may be blurrier, but latent space interpolation is more meaningful | Produces high-quality samples |
Output Diversity | Sometimes experience mode collapse, which results in little variability | Less prone to mode collapse, offering better coverage of the data distribution | The outputs are coherent, contextually relevant, and diverse |
Mathematical Basis | Rooted in game theory and Nash equilibrium | Based on variational inference and a Bayesian framework | Based on linear algebra, self-attention mechanism, multi-head attention, positional encoding and feed-forward networks |
Common Applications | Image synthesis, style transfer, super-resolution, art generation | Data compression, anomaly detection, feature learning, semi-supervised learning | Natural language processing, speech recognition, Named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, etc. |
The use of generative AI is well-witnessed in practice and research, and the right option would be Deterministic Networks or GANs, depending on practical needs. However, if we had to communicate the advantages and disadvantages of these tools, picture this: Use GANs for image generation, VAE for creativity, and transformers for text and multimodel data generation and handling capabilities.
Generative AI developers must be employed to utilize the capabilities of the given models fully. In cases where businesses wish to produce photorealistic images, design text solutions, or build artificial datasets, generative AI specialists ensure that these projects do not fail.
Hyqoo sources talent from all over the world to meet your requirements. The talented professionals are highly skilled, and the best part is that you close the vacancy within 2-3 days. If you are looking for remote employees, share your requirements today to hire the best!
Generative AI, or Gen AI, is a type of AI capable of creating a wide range of content, such as text, images, audio, and synthetic data, in response to a user’s prompt. Gen AI relies on machine learning models called deep learning models.
GANs, or Generative Adversarial Networks, are a kind of neural network, a machine learning model specifically created to resemble the composition and operations of the human brain.
VAEs, or Variational Autoencoders, are generative models specifically designed to produce new samples and capture a dataset’s underlying probability distribution.